Partial knee replacement at Cambridge Hospital
- Overview
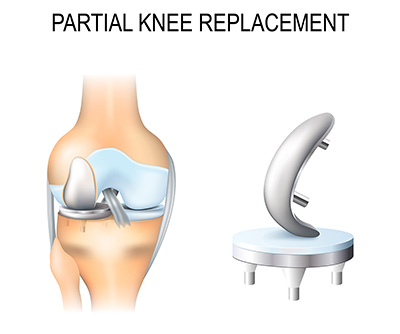
Partial knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement (UKR), is a surgical procedure in which only the damaged part of the knee joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint.
What is a partial knee replacement?
Partial knee replacement, or unicompartmental knee replacement, is a surgical procedure to remove and replace only the damaged part of the knee joint with an artificial joint. In comparison, knee replacement or total knee replacement, is a surgical procedure that removes the entire knee joint and replaces it with an artificial joint.
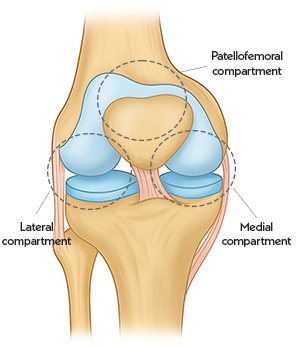
Your knee is made up of three main compartments:
- Medial - the inside part of your knee.
- Lateral - the outside part of your knee
- Patellofemoral - the front of your knee between your kneecap (patella) and thighbone (femur).
The ends of the bones in the knee joint are covered with a smooth, protective tissue called articular cartilage. This cartilage acts as a cushion, allowing the bones to glide easily against each other during movement. Sometimes the articular cartilage can wear down or become damaged. Without the protection of this lining, the rough surfaces of the bones are exposed and rub against each other, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
The cartilage can wear down or become damaged due to:
- Osteoarthritis: when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: when the body's immune system attacks the lining of the joints (synovium).
- An injury to the knee, such as a fracture, ligament tear, or meniscus injury.
If your knee is damaged in only one compartment, you may be suitable for partial knee replacement.
Partial knee replacement is most commonly performed on the medial (inner) compartment of the knee. It can also be done on the lateral (outer) or patellofemoral (kneecap) compartments, depending on the location of the damage.
Types of partial knee replacement
There are three types of partial knee replacement:
- Medical Unicompartmental Knee Replacement: Replaces the inner part (medial) of the knee.
- Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Replacement: Replaces the outer part (lateral) of the knee.
- Patellofemoral Knee Replacement: Replaces the underside of the kneecap (patella) and the groove at the end of the thighbone (femur) where the kneecap glides.
- Bicompartmental Knee Replacement: Replaces two of the three compartments of the knee, usually the medial and patellofemoral compartments.
Is a partial knee replacement right for me?
Your consultant may recommend a partial knee replacement if:
- Your pain is localised - for example, you feel pain on one side of the knee or only during certain movements.
- You have arthritis in one compartment of the knee.
- Your ligaments are intact and stable, particularly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial/lateral collateral ligaments, which help keep your knee steady.
- You have a good range of motion.
- You are not significantly overweight - maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the implant and helps it last longer.
- You’ve tried alternative treatments, such as physiotherapy, pain relief, walking aids or joint injections, and they haven’t helped.
What happens during partial knee replacement surgery?
The day of your surgery
At the hospital, we’ll show you to your hospital room, where one of our healthcare team members will meet you to explain each stage of your treatment and recovery. They’ll take notes on your general health, medical and surgical history and ask if you have any allergies. Your blood pressure, pulse and temperature will be taken, and an identification band with your name and hospital number on it will be placed on your wrist.
Your consultant will visit you. And if you haven’t signed a consent form already, you’ll be asked to sign one by your consultant. This is to confirm that you understand the details of your operation, including the benefits and risks associated with it, both during and after your procedure.
When it’s time to go to the operating theatre, our ward staff will take you. There, our theatre staff will take you to the anaesthetic room. If you are concerned about anything, please ask. We understand this can be a very stressful time.
During the surgery
Partial knee replacement surgery typically lasts between 1.5 and 2 hours. The operation can be performed under general anaesthetic or spinal anaesthetic with sedation. Your consultant and hospital team will discuss which type of anaesthesia is best for you.
Traditional partial knee replacement surgery
- Your surgeon will make an incision (cut) in the front of your knee to access the joint.
- They will examine all three compartments of your knee to confirm that damage is limited to one compartment (medial, lateral or patellofemoral).
- The damaged cartilage and bone will be removed.
- Metal caps or implants are then placed over the prepared bone surfaces, and the bone is fixed to the implant using an acrylic cement or a special coating that allows the artificial joint to bond directly to the bone over time.
- The surgeon will close the incision with staples or stitches.
Robotic-assisted partial knee replacement
Robotic-assisted partial knee replacement uses advanced technology to help your surgeon work more accurately. This method can lead to faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and better results for many patients.
Mako® Robotic-Arm assisted surgery
- Before your surgery, you will have a CT scan of your knee to create a 3D model of your knee joint. The 3D model is loaded into the Mako® system software to create a personalised surgical plan, which your surgeon will use during your surgery. The plan includes the implant's exact size, placement, and positioning.
- Your surgeon will make an incision (cut) on the front of the knee to access the joint.
- Your surgeon will use the Mako® robotic arm to remove the damaged cartilage and bone from the knee.
- The artificial joint is implanted. The robotic arm guides your surgeon to stay within the pre-planned boundaries set by the 3D model, allowing for accurate implant positioning.
- The implant is fixed to the bones using an acrylic cement or a special coating that allows the artificial joint to bond directly to the bone over time.
- Your surgeon will check the new joint's stability, alignment, and movement before closing the cut with stitches or surgical clips and applying a padded dressing.
Find out more about Mako® Robotic-arm assisted partial knee replacement.
After the operation
Once your operation is over, you’ll be taken to the recovery room where you will wake from the anaesthetic. Your wound, blood pressure and pulse will be checked carefully. You will have a large dressing covering your wound. You may have a small tube coming out of your wound; this is used to drain any excess fluid from the inside of the wound.
You may also have a drip (infusion) going into your arm. This will keep you hydrated until you can drink, and it can also provide pain relief. When you are stable and comfortable, a nurse will take you back to your hospital room.
Recovery from partial knee replacement
Getting up for the first time
We understand that you may be anxious or worried about getting up, but we will do all we can to help and reassure you. Don’t worry, a member of our healthcare team will be there to help you, whenever you are ready. The reason for getting you moving is to improve your circulation and avoid stiffness.
You may be feeling tender and sore, but you can get pain relief medication to manage any discomfort - ask one of the nurses if you experience any pain. Once out of bed, continue to wear support stockings to help improve your circulation. The physiotherapists will work with you during your stay to help you achieve the best possible start with your new joint.
Going home after partial knee placement
As partial knee replacement is less invasive than total knee replacement, patients usually go home sooner and return to normal activities earlier. You may need to stay in the hospital one to three days. Before leaving, you will have an X-ray of your new knee to check its position.
A physiotherapist will give you some exercises to help get your new knee moving. These are important to help you make a good recovery. The therapist will also show you how to walk up and down stairs and make sure you are confident in doing this before you go home. You won’t be able to drive, so you will need someone to come and take you home from the hospital.
When you return home, you may need assistance with shopping and household chores. It’s a good idea to arrange for someone to stay with you, or at least look in on you daily for at least a week.
It’s usual to return to see your consultant as an outpatient after your operation. You may also need to have stitches removed. You’ll be given information about these appointments before you go home. We’ll also give you some pain relief medication to take with you.
When you get home, it is essential to rest. However, it’s also important to aim to gradually increase your physical activity each day, so you should continue with the exercises the physiotherapist showed you. These will help to reduce stiffness and strengthen your legs. You will need to keep using crutches or a walking stick for a while. To help you manage and increase mobility, it’s recommended that you take any pain relief medication we have prescribed. Continue taking this until you are pain-free.
So you don’t damage your new knee, and to help your wound heal, you should:
- Use the shower instead of the bath
- Keep wearing your support stockings - you may have to do so for 4 to 6 weeks.
Getting back to normal
Everyone heals differently. You will continue to improve over the next 6 to 8 months. Your scar should fade to a thin white line.
Depending on what type of job you do, you should be able to return to work within eight to twelve weeks. You may want to think about a phased return to work.
After your follow-up visit with your surgeon, you should be released to drive, but only if you can comfortably operate the pedals and control your car in all situations. This includes an emergency stop. If you are in any doubt about your insurance cover, it’s best to contact your insurance company.
Complications of a partial knee replacement
Most people make a good recovery and return to normal activities following partial knee replacement surgery. As with any surgery, there can be complications, such as:
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Infection of the surgical site (incision)
- Scarring
- Blood clots (DVT - deep vein thrombosis)
- Difficulty passing urine
- Chest infection
- Heart attack
- Stroke
Risks specific to partial knee replacement surgery are:
- Nerve damage
- Damage to blood vessels
- Bearing dislocation
- Infection in the knee
- Loosening of the components
- Severe pain, stiffness and loss of use of the knee (complex regional pain syndrome)
Partial knee replacement consultants at Cambridge Hospital
4 Trumpington Road, Cambridge, CB2 8AF
Guide price
| Initial consultation | from £210 | |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | If needed to determine treatment plan | |
| Treatment | £19,795 | |
| Pre-assessment | Included | |
| Main treatment | Included | |
| Post-discharge care | Included | |
| Pre-assessment, Main treatment and Post-discharge care | £19,795 | |
| Guide price | £20,005 | |
The guide price
stated above is an approximation of the cost of treatment only. The final price
may vary according to Consultant fees, prosthesis or drugs used and any
pre-existing medical conditions which may alter your care pathway.
You will be given a fixed all-inclusive price for treatment following
your initial consultation with a Consultant.
Ways to pay
Nuffield Health promise
Our prices are all-inclusive. We will equal any comparable price. There are no time limits on your aftercare.
Paying for yourself
There are no hidden costs in our treatment prices. The price you see is the price you pay.
Find out morePersonal medical loan
Spread the cost of your treatment with a 10, 12 or 24 month 0% personal medical loan.
Find out moreMedical insurance
We work with you and your insurance provider to get you the treatment you need quickly
Find out more